Miscellaneous Legal Requirements for Companies in Pakistan
Establishing and maintaining a company in Pakistan is not just about getting registered—it’s about staying compliant every step of the way. Once your business is incorporated with the Securities and Exchange Commission of Pakistan (SECP), a wide range of legal and regulatory obligations must be fulfilled on an ongoing basis to ensure your operations remain legitimate, transparent, and in good standing with the relevant authorities.
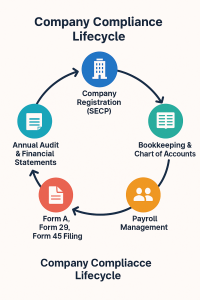
These miscellaneous compliance requirements include, but are not limited to, maintaining proper books of accounts, filing timely tax returns, updating statutory records, conducting annual audits (where applicable), ensuring payroll deductions are accurate and reported, and submitting necessary forms to SECP such as Form A, Form 29, and Form 45. Failure to meet these obligations can lead to penalties, reputational harm, and even the risk of business suspension.
At Arshad & Associates, we specialize in guiding startups, SMEs, and established enterprises through every phase of their business lifecycle—from setup to ongoing compliance. Our expert team offers end-to-end support tailored to your needs, including:
- 📘 Accurate and up-to-date bookkeeping using modern double-entry accounting standards
- 🧾 Expert taxation services covering income tax, sales tax, and withholding tax compliance
- 👥 Efficient payroll management, ensuring proper salary calculations, deductions, and statutory filings
- 💻 Seamless accounting software integration with platforms like QuickBooks, Xero, and ZohoBooks
- 📄 Regulatory filings and SECP compliance, including timely submissions of corporate forms and annual returns
Whether you’re starting fresh or scaling your operations, our goal is to help you navigate Pakistan’s legal framework with clarity and confidence. Let us handle your compliance burden—so you can focus on building and growing your business.
Understanding the Legal Framework
Navigating the legal landscape of doing business in Pakistan requires a clear understanding of the country’s corporate, tax, and regulatory environment. From the moment a company is incorporated, it becomes subject to a complex web of obligations governed by authorities such as the Securities and Exchange Commission of Pakistan (SECP), the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR), and provincial revenue boards. These laws dictate how a company must operate, report, and maintain transparency across all functions—whether it’s bookkeeping, taxation, payroll, or statutory compliance.
This section aims to provide a foundational overview of the key laws and regulations that shape business operations in Pakistan, helping entrepreneurs and business owners make informed, compliant decisions that support long-term growth and sustainability.
The SECP’s Role in Company Regulation
The Securities and Exchange Commission of Pakistan (SECP) is the primary regulatory authority responsible for overseeing corporate sector operations, company registrations, and enforcing corporate governance in Pakistan. It plays a critical role in regulating businesses under the Companies Act, 2017, and ensuring that companies operate transparently, ethically, and in accordance with the law.
Once a company is registered with SECP, the journey of compliance begins—not just a one-time task, but a continuous process. These ongoing obligations include maintaining updated statutory records such as registers of members, directors, and shareholding structures, as well as preparing and preserving minutes of meetings and resolutions. Companies are also required to submit periodic filings such as Form A (annual returns), Form 29 (changes in directors or officers), Form 45 (particulars of beneficial ownership), and audited financial statements.
Additionally, businesses must ensure timely compliance with any changes in company structure, such as share transfers, amendments to the Memorandum or Articles of Association, or alterations in business objectives. Non-compliance with SECP regulations can result in penalties, disqualification of directors, and even legal proceedings.
Understanding and adhering to these SECP requirements is essential for maintaining your company’s legal standing, building investor trust, and avoiding unnecessary legal hurdles. This is where the expertise of professionals like Arshad & Associates becomes invaluable, ensuring that your business remains compliant, transparent, and well-managed at every step.
Common Company Types
When registering a business in Pakistan, choosing the right company structure is one of the most important decisions you’ll make. The Securities and Exchange Commission of Pakistan (SECP) offers several types of company structures, each with distinct characteristics, legal implications, and compliance requirements. Below are the most commonly registered types:
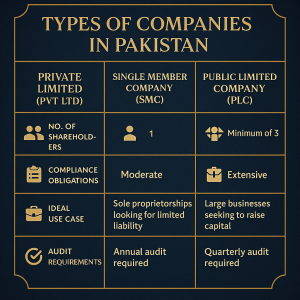
1. Private Limited Company (Pvt Ltd)
A Private Limited Company is one of the most popular business structures in Pakistan, particularly among startups, SMEs, and family-owned businesses. It is registered under the Companies Act, 2017 and must have a minimum of two and a maximum of fifty shareholders. The liability of each shareholder is limited to the amount unpaid on their shares, which provides financial protection to the owners.
This type of company cannot offer its shares to the public and cannot be listed on a stock exchange. However, it enjoys several benefits such as limited liability, better credibility with banks and investors, and a structured corporate framework. The management is handled by a board of directors, and companies are required to maintain proper statutory books, file annual returns, and conduct annual general meetings (AGMs).
Ideal for: Medium-sized businesses, partnerships seeking liability protection, or growing startups looking to attract private investors.
2. Single Member Company (SMC)
A Single Member Company (SMC) is a specialized type of private limited company that allows a single individual to incorporate a company. It is particularly beneficial for solo entrepreneurs who wish to establish a formal corporate identity while retaining full ownership and control of the business.
The SECP has specific provisions for SMCs under the Companies Act, 2017, allowing them to operate as legal entities with limited liability. Although there is only one shareholder, the law requires the appointment of a nominee director who takes over in case of the owner’s death or incapacity. SMCs are required to file annual returns, maintain proper accounting records, and comply with tax and legal regulations like any other incorporated company.
Ideal for: Freelancers, consultants, professionals, and solo business owners who want liability protection and a more structured business identity.
3. Public Limited Company (PLC)
A Public Limited Company is suitable for large-scale businesses that wish to raise capital from the public through stock offerings. There are two types of PLCs: listed and unlisted. A listed PLC is one that is registered with a stock exchange and can offer shares to the general public, while an unlisted PLC is not traded on the stock exchange but may still raise funds through private placements.
Public limited companies are required to have at least three directors and a minimum of seven shareholders, with no upper limit. Due to their size and access to public funds, PLCs are subjected to stricter regulatory requirements, including detailed financial disclosures, regular audits, board meetings, and compliance with corporate governance codes.
Ideal for: Large enterprises aiming to expand significantly, attract public investment, or eventually get listed on the Pakistan Stock Exchange (PSX).
Core Bookkeeping and Accounting Requirements
Accurate bookkeeping and sound accounting practices form the backbone of every legally compliant and financially healthy business in Pakistan. Regardless of the size or structure of your company—whether it’s a Private Limited Company, Single Member Company, or Public Limited Company—you are legally required to maintain comprehensive financial records that reflect the true state of your business affairs.
The Companies Act, 2017 mandates that all registered companies in Pakistan must maintain proper books of accounts, which should accurately record:
- All sums of money received and expended by the company
- Details of assets and liabilities
- Records of sales and purchases
- Details related to income and expenditures
- Payroll records and employee benefit liabilities
- Statutory deductions such as income tax, sales tax, and withholding taxes
These records must be maintained in a structured and systematic format and preserved at the company’s registered office or another location approved by the board. The accounting books should be kept up to date on a day-to-day basis and must comply with the principles of double-entry bookkeeping, ensuring that every financial transaction is recorded with equal and opposite entries in two or more accounts.
Additionally, companies must prepare financial statements at the end of each financial year, which include:
- A Balance Sheet
- Profit and Loss Account (Income Statement)
- Cash Flow Statement
- Statement of Changes in Equity
- Notes to the Financial Statements
These statements must be approved by the Board of Directors and, in many cases, audited by a registered Chartered Accountant, especially for Private Limited Companies and all Public Limited Companies.
For tax purposes, accurate bookkeeping is crucial. The Federal Board of Revenue (FBR) requires that all income and expenses are properly documented for filing annual tax returns, sales tax returns, and withholding statements. Poor or incomplete bookkeeping can lead to penalties, incorrect tax filings, and compliance issues.
Moreover, payroll accounting is a critical component, especially for businesses with employees. This includes maintaining salary records, computing deductions (such as income tax, EOBI, and social security), and issuing payslips. These records must also align with the payroll tax returns submitted to the authorities.
To streamline these tasks and minimize human error, many companies in Pakistan integrate accounting software solutions such as QuickBooks, Xero, Zoho Books, or Tally ERP, which help maintain ledgers, automate reconciliations, generate tax reports, and manage payroll efficiently.
At Arshad & Associates, we help businesses not only stay compliant with all these statutory bookkeeping requirements but also unlock real insights from their numbers. Our expert accountants and bookkeepers assist in setting up the chart of accounts, reconciling bank statements, handling journal entries, managing ledgers, and generating timely financial reports—ensuring full transparency and control.
Mandatory Bookkeeping Practices
All registered businesses in Pakistan, regardless of their size or industry, are legally obligated to maintain accurate and up-to-date bookkeeping records. These records form the financial backbone of the organization and must capture every financial transaction that takes place within the business. From daily sales and purchases to payroll expenses and tax deductions, each transaction must be properly documented, categorized, and stored in accordance with local laws and international accounting standards.
Maintaining these records involves making a bookkeeping entry for every financial activity—whether it’s receiving income, paying suppliers, recording employee salaries, or reconciling bank statements. These entries must be logged consistently and accurately to ensure the books reflect the true financial position of the business.
To achieve this level of accuracy and transparency, companies must follow established accounting principles such as double entry bookkeeping, where each transaction affects at least two accounts—for example, a debit in one and a credit in another. This method helps reduce errors and provides a more complete view of a company’s financial health.
In addition, businesses are encouraged to follow the accrual accounting method, which records income and expenses when they are incurred rather than when cash is exchanged. This approach gives a more realistic picture of financial performance during a specific period and is particularly important for preparing financial statements, managing cash flow, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Proper bookkeeping is not just a statutory requirement—it is a critical tool for business decision-making, budgeting, forecasting, and tax planning. At Arshad & Associates, we assist clients in setting up and maintaining meticulous bookkeeping systems that align with the latest legal requirements and industry best practices, helping businesses stay audit-ready and financially organized at all times.
Chart of Accounts and Ledger Account Maintenance
A **chart of accounts** tailored to your industry is essential. Every **ledger account** must be updated regularly to reflect accurate financial positions.
General Ledger and Accounting Cycle
A well-structured and industry-specific chart of accounts is a fundamental component of an effective bookkeeping system. The chart of accounts serves as the master blueprint for organizing all financial transactions within your business. It categorizes every type of income, expense, asset, liability, and equity item into a systematic list of accounts—each assigned a unique code for easy identification and tracking. Whether you’re in retail, manufacturing, services, or the tech sector, having a chart of accounts that is tailored to your specific industry ensures that your financial reporting is not only accurate but also meaningful and actionable.
Each item listed in the chart of accounts leads to a corresponding ledger account, which records the detailed activity for that category over time. For example, the “Salaries Expense” ledger will reflect every salary transaction made, while the “Accounts Receivable” ledger will show all outstanding customer invoices. These ledger accounts must be updated regularly—ideally on a daily or weekly basis—depending on your volume of transactions.
Keeping your ledger accounts current is critical for several reasons. First, it provides an up-to-date view of your company’s financial health, which is essential for decision-making and cash flow management. Second, it ensures that your financial statements—such as the balance sheet and income statement—accurately reflect your business’s performance and position at any given time. Third, it helps in reconciling discrepancies, preparing tax returns, and ensuring compliance with regulatory authorities like the SECP and FBR.
Neglecting to maintain accurate ledgers can result in financial misstatements, missed tax deductions, incorrect budgeting, and even legal complications. That’s why it’s important to invest in a proper bookkeeping system and, if possible, integrate it with accounting software that automates ledger maintenance, generates real-time reports, and supports audit trails.
Tax Compliance and Filing Obligations
In Pakistan, staying compliant with tax laws is not just a legal responsibility—it’s a critical aspect of running a sustainable and transparent business. Whether you’re a sole proprietor, a partnership, or a registered company, tax compliance is essential to avoid penalties, build credibility, and maintain smooth financial operations. The Federal Board of Revenue (FBR) oversees the enforcement of tax regulations at the national level, while provincial revenue authorities handle region-specific levies such as sales tax on services.
Filing accurate and timely tax returns, deducting and depositing withholding taxes, issuing proper tax invoices, and maintaining audit-ready records are just some of the many obligations businesses must meet. With evolving laws, digital portals, and changing tax rates, it’s vital for business owners to stay informed and work with professionals who can ensure full compliance across all areas of taxation—including income tax, sales tax, and payroll-related taxes.
This section outlines the key tax compliance requirements and filing obligations every business in Pakistan must adhere to—helping you stay legally sound, financially optimized, and audit-ready at all times.
Income Tax Requirements
All businesses operating in Pakistan—whether they are sole proprietorships, partnerships, or incorporated companies—are legally required to calculate income tax in accordance with the applicable taxable income slab defined by the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR). The amount of tax payable is determined by the net taxable income, which is calculated after deducting all allowable business expenses, depreciation, tax credits, and applicable exemptions from the gross income. The tax slab or rate varies depending on the type and scale of the business entity, and it is essential to stay updated on the latest changes introduced in the Finance Act each fiscal year.

Once the taxable income has been computed, businesses must prepare and submit an income tax return through the FBR’s online IRIS portal. This return must include detailed financial statements, tax computation, particulars of income from all sources—including business profits, rental income, and capital gains—and any applicable withholding tax adjustments.
Timely and accurate submission of income tax returns is not only a legal obligation but also critical for maintaining a strong compliance profile. Filing your return late or submitting incorrect/incomplete information can lead to a range of consequences, including:
- Heavy penalties and default surcharges
- Disqualification from the Active Taxpayers List (ATL)
- Higher tax deduction rates by other entities
- Increased likelihood of audits and scrutiny from FBR
Maintaining proper documentation and ensuring precise calculation of income tax is key to avoiding these risks. At Arshad & Associates, our experienced tax consultants help businesses with detailed income assessments, correct application of tax slabs, online filing through IRIS, and navigating the complexities of Pakistan’s tax regulations—ensuring full compliance and peace of mind.
Key Steps:
Successfully meeting your income tax obligations in Pakistan involves several important steps. Each step ensures that your business not only fulfills its legal requirements but also takes full advantage of available deductions, credits, and incentives. Below is a detailed overview of the key steps involved in the income tax compliance process:
✅ Income Tax Registration
The first step toward compliance is obtaining a National Tax Number (NTN) by registering your business with the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR). Without this registration, a business cannot legally operate, open a bank account, or enter into contracts. The registration process requires submission of company documents, CNIC copies of directors or proprietors, proof of business address, and a valid email address. Once registered, your business becomes eligible to file returns, claim tax credits, and appear on the Active Taxpayers List (ATL).
📊 Tracking Capital Gains and Rental Income
It’s essential for businesses and individuals to monitor and report all sources of income—not just operational revenue. This includes capital gains earned from the sale of property, shares, or other investments, and rental income from leasing property or assets. These additional income streams are taxed differently and may require separate reporting in the income tax return. Keeping a detailed record of acquisition costs, sale proceeds, and related expenses ensures accurate computation and compliance with FBR requirements.
💻 Filing via Online Tax Return Systems
The FBR has mandated the use of its IRIS portal for electronically submitting income tax returns. This system simplifies filing by offering a step-by-step process to enter income details, upload supporting documents, claim tax credits, and compute final tax liability. The online system also facilitates submission of wealth statements, reconciliation statements, and tax challans. Businesses must file returns annually, while some may also be required to file quarterly advance tax payments.
📘 Understanding Income Tax Rates and Income Tax Ordinance Updates
Tax laws in Pakistan evolve frequently with changes introduced in each Finance Bill and through amendments to the Income Tax Ordinance, 2001. Staying updated on the latest income tax rates, slabs, exemptions, and regulatory changes is crucial for accurate tax planning and filing. For example, different rates apply to companies, AOPs, and individuals, and tax credits may be available for specific sectors such as IT exports, manufacturing, or green energy.
Businesses must regularly review FBR notifications, SROs (Statutory Regulatory Orders), and changes in the Finance Act to ensure they are applying the correct rates and claiming all applicable benefits.
Withholding Tax Compliance
Withholding Tax Compliance
In Pakistan, withholding tax (WHT) plays a significant role in the overall tax structure and serves as a major source of revenue for the government. It is a tax deducted at source—meaning businesses are legally required to deduct a specified percentage of tax from payments made to certain parties, such as suppliers, service providers, contractors, consultants, and employees. These deductions are then deposited with the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR) on behalf of the recipients.
If your business is making routine payments for services rendered, purchase of goods, rent, salaries, commissions, or contracts, you may be categorized as a withholding agent under Pakistan’s tax laws. As a withholding agent, your business has the obligation to not only deduct the applicable tax before making payments but also to file periodic statements and deposit the withheld tax on time. Failure to do so can result in significant penalties, additional tax liability, disallowance of expenses, and audit notices from FBR.
Here’s why understanding and complying with withholding tax obligations is critical:
- Legal Liability: Once you fall under the definition of a withholding agent, non-compliance can make your business personally liable for unpaid taxes.
- Expense Disallowance: If withholding tax is not deducted or deposited correctly, FBR may disallow related expenses while assessing your income tax return—leading to increased tax payable.
- Higher Deduction Rates: Payments to persons not listed on the Active Taxpayers List (ATL) attract higher deduction rates, making it essential to verify the tax status of vendors before payments.
- Monthly and Annual Filings: Businesses must submit monthly or quarterly withholding tax statements (under Section 165 of the Income Tax Ordinance) and ensure all challans and documentation are up to date.
The following are common transactions where WHT is typically applicable:
- Salaries and Employee Compensation
- Rent Paid for Office or Commercial Spaces
- Professional Fees to Accountants, Lawyers, or Consultants
- Payments to Contractors or Freelancers
- Purchase of Goods Above Prescribed Thresholds
- Utility Payments in Some Cases
Each category has its own prescribed withholding rate, which is subject to frequent updates via Finance Bills and Statutory Regulatory Orders (SROs). Businesses must therefore stay updated on current tax rates and compliance deadlines.
Payroll Management System Requirements
An efficient and compliant payroll management system is vital for every business in Pakistan that employs staff, whether full-time, part-time, or contractual. Managing payroll goes far beyond issuing salaries—it involves calculating gross and net pay, handling tax deductions, complying with statutory contributions (such as EOBI and social security), and maintaining detailed employee compensation records. Moreover, businesses must ensure that payroll data is accurately recorded in their accounting system and aligned with their monthly tax filings.
In Pakistan, the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR), along with provincial social security institutions, impose strict requirements for tax withholding on salaries, submission of monthly salary statements, and payment of payroll-related taxes. Failure to comply can result in penalties, legal disputes, and loss of employee trust.
This section outlines the key legal, accounting, and operational requirements for setting up and maintaining a compliant and effective payroll system—helping business owners streamline HR operations, reduce risk, and ensure smooth collaboration with government authorities.
Payroll Compliance in Pakistan
A well-structured and fully compliant payroll management system is not just a best practice—it is a legal requirement for all registered businesses in Pakistan, particularly for companies with multiple employees on their payroll. As your workforce grows, so do your responsibilities related to salary disbursement, tax deductions, employee benefits, and government reporting. Without an organized system in place, managing payroll manually can lead to errors, delayed payments, non-compliance with tax laws, and dissatisfaction among employees.
A reliable payroll system ensures that each employee is compensated accurately and on time while complying with all applicable labor laws, income tax regulations, and statutory deductions such as EOBI (Employees’ Old-Age Benefits Institution) and Social Security contributions. It should also handle tasks such as the generation of payslips, salary slips, calculation of bonuses and overtime, leave encashment, and severance pay in accordance with employment contracts and company policies.
Furthermore, the payroll process must be integrated with the company’s accounting and bookkeeping systems to ensure that salary expenses, tax liabilities, and deductions are properly recorded in the financial books. Businesses are also required to submit monthly salary tax withholding statements to the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR), making payroll accuracy a key aspect of overall tax compliance.
Key Components of a Compliant Payroll Management System
Implementing an effective payroll system involves several critical components that ensure legal compliance, employee satisfaction, and financial accuracy. Below are the key functions every business must incorporate into its payroll management framework:
📄 Payroll Slip Issuance
One of the foundational elements of any payroll system is the timely and consistent issuance of payroll slips or salary statements to employees. A payroll slip details the employee’s gross earnings, all applicable deductions (such as income tax, EOBI, and social security), and the resulting net salary. It also includes information about bonuses, overtime, and any leave deductions. Issuing clear, itemized salary slips not only ensures transparency but also helps employees understand how their pay is calculated and enhances trust in the organization. In Pakistan, providing salary slips is also considered part of best HR and tax practices, especially for companies preparing for audits or regulatory reviews.
💰 Payroll Tax Calculation and Deductions
A key legal requirement for all businesses is the calculation and deduction of payroll taxes before disbursing salaries. These include income tax deductions under section 149 of the Income Tax Ordinance, as well as statutory contributions such as Employees’ Old-Age Benefits Institution (EOBI) and Social Security where applicable. The correct application of tax slabs, exemptions, and rebates is necessary to ensure that each employee’s tax withholding is accurate. Errors in tax deductions can result in non-compliance penalties, inaccurate tax filings, and employee grievances. A robust payroll system automates this process to minimize errors and ensure timely deposit of withheld taxes to the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR).
🔍 Maintaining a Transparent Paycheck Estimator
Modern businesses are increasingly adopting digital tools like a paycheck estimator to offer greater transparency to employees regarding their compensation structure. A paycheck estimator allows employees to preview their salary breakdown—including basic pay, allowances, deductions, and net take-home—before the actual salary is processed. This is especially useful in organizations where salaries vary due to commissions, overtime, or project-based bonuses. Maintaining a transparent payroll process fosters trust, improves employee morale, and reduces payroll-related disputes.
📊 Adhering to Single Touch Payroll Practices
Single Touch Payroll (STP) refers to a streamlined payroll reporting method where employee salary and tax information is reported to the tax authorities at the time of salary disbursement. While STP is not yet fully mandated in Pakistan as it is in some other countries like Australia, adopting STP-aligned practices is increasingly encouraged—especially for medium to large enterprises aiming for digital transformation and audit readiness. These practices include real-time payroll updates, integrated tax reporting, and instant submission of withholding statements through online platforms such as the FBR IRIS portal.
Monthly and Annual Submissions
Employers in Pakistan are legally obligated to handle not just salary disbursements, but also the timely submission of withholding tax and various employee tax contributions each month. This includes deducting income tax at source under Section 149 of the Income Tax Ordinance, 2001, as well as calculating contributions for statutory bodies such as EOBI (Employees’ Old-Age Benefits Institution) and provincial social security institutions, where applicable.
Once these deductions are made, the employer must deposit the withheld taxes into the government treasury using designated challan forms and submit monthly statements through the FBR’s IRIS portal. These statements confirm the amount deducted from employee salaries and the corresponding payments made on behalf of the employees.
Beyond monthly compliance, employers must also conduct a year-end reconciliation of all payroll-related taxes and contributions. This is done as part of the annual income tax return filing process with the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR). The reconciliation ensures that the cumulative amounts withheld, reported, and deposited throughout the year match the actual payroll and tax records.
Failure to meet these monthly and annual obligations can result in serious penalties, legal complications, and disqualification from the FBR Active Taxpayers List (ATL). Employers may also face issues during audits if payroll records and tax submissions are not properly aligned.
Accounting Software Integration
In today’s fast-paced business environment, manual bookkeeping and outdated spreadsheets are no longer sufficient for maintaining financial accuracy or meeting compliance requirements. Efficient accounting software integration is essential for businesses in Pakistan to streamline operations, reduce errors, and maintain real-time visibility into their financial performance. Whether you’re managing sales, expenses, payroll, or taxes, integrating modern accounting software allows you to automate repetitive tasks, generate detailed financial reports, and stay compliant with regulations set by the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR) and Securities and Exchange Commission of Pakistan (SECP).
With tools like QuickBooks, Xero, Zoho Books, Wave, and Odoo, businesses can maintain a centralized financial system that connects payroll, tax filings, bank reconciliations, invoicing, and budgeting—all in one platform. This not only saves time but also ensures that your chart of accounts, general ledger, and financial statements are always accurate and audit-ready.
QuickBooks, Xero, and ZohoBooks
Integrating modern accounting software such as QuickBooks Online, Xero Accounting, or ZohoBooks is a vital step for businesses that aim to enhance financial accuracy, improve operational efficiency, and ensure ongoing regulatory compliance in Pakistan. These cloud-based platforms are designed to simplify complex accounting tasks such as recording transactions, managing payroll, generating financial reports, filing tax returns, and performing real-time bank reconciliations.
By leveraging the power of automation and centralized data management, these tools significantly reduce the risk of manual errors, save valuable time, and allow business owners and finance teams to focus on strategic decision-making instead of routine data entry. In addition, many of these accounting systems are regularly updated to stay in sync with changes in tax regulations introduced by the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR), making them ideal for keeping up with compliance requirements such as income tax, sales tax, and withholding tax filings.
Moreover, features like dashboard reporting, automated journal entries, built-in audit trails, and secure multi-user access help businesses gain better control over their finances and maintain full visibility of cash flow, expenses, and profitability. These tools also support seamless integration with other systems like eCommerce platforms, payroll services, and point-of-sale systems, creating a unified financial ecosystem.
At Arshad & Associates, we assist businesses in selecting the right accounting software, customizing the chart of accounts, integrating with banking APIs, and training staff to ensure the software is used to its full potential. With the right setup and support, your business can move from reactive bookkeeping to proactive financial management—while remaining fully compliant with Pakistan’s evolving financial regulations.
Software Features:
Modern accounting platforms come equipped with robust features that simplify financial management while ensuring regulatory compliance. Below are some of the most impactful tools that businesses in Pakistan can leverage through cloud-based accounting software integration:
☁️ QuickBooks Manage Payroll Cloud Services
QuickBooks Online offers comprehensive cloud-based payroll management services, making it easier for businesses to process salaries, calculate payroll taxes, and issue payslips—anytime, from anywhere. These services automatically compute employee earnings, deductions (like income tax and EOBI), and contributions, and sync all payroll data with your accounting ledgers in real time. Employers can also schedule payments, generate compliance-ready payroll reports, and ensure accurate filing with regulatory bodies, reducing the risk of human error or non-compliance.
🏦 Real-Time Bank Reconciliation
Integrated accounting systems like Xero, ZohoBooks, and QuickBooks Online allow for real-time bank reconciliation, meaning businesses can connect their bank accounts directly to the software. This feature automatically imports and categorizes transactions, saving hours of manual entry and drastically reducing reconciliation errors. Real-time syncing enables business owners to track cash flow on a daily basis, spot inconsistencies quickly, and ensure that every entry in the general ledger matches the bank statement—making your books audit-ready at all times.
📘 Automated Double Entry Accounting
One of the core strengths of professional accounting software is automated double entry accounting, which ensures every transaction is recorded with equal and opposite entries in relevant accounts. This not only upholds the integrity of financial data but also allows for seamless tracking of assets, liabilities, income, and expenses. Whether you’re recording a customer invoice, making a supplier payment, or logging depreciation, the system automatically updates both the debit and credit sides—minimizing the chance of errors and maintaining full transparency across your financial records.
📄 Seamless Report Generation for Income Tax Filing
Software tools like QuickBooks, Xero, and ZohoBooks simplify income tax preparation by generating detailed financial reports that comply with Pakistan’s tax regulations. These reports include profit and loss statements, balance sheets, trial balances, sales tax summaries, and withholding tax schedules—making it easy to file tax returns through the FBR IRIS system. Having access to well-organized reports also helps businesses respond quickly to audit queries, track financial performance, and forecast tax liabilities with greater accuracy.
Filing Statutory Returns and SECP Compliance
In addition to maintaining accurate bookkeeping records and fulfilling regular tax compliance obligations, companies in Pakistan are also required to submit a range of statutory filings to the Securities and Exchange Commission of Pakistan (SECP). These filings ensure that the company’s corporate structure, governance framework, and financial disclosures remain transparent and up to date in the public record. Timely submission of these documents is not just a legal formality—it is essential for maintaining an active company status and avoiding regulatory complications.
Some of the most important statutory forms and filings include:
- 📄 Form-A (Annual Return):
This form must be filed annually and contains details about the company’s shareholding structure, directors, registered address, and auditors. It serves as a yearly confirmation of corporate details held with SECP. Every private and public limited company is required to file Form-A within 30 days of holding its Annual General Meeting (AGM). - 👥 Form-29 (Changes in Directors or Officers):
Whenever there is an appointment, resignation, change in designation, or reappointment of directors, chief executive officers, or company secretaries, it must be reported to SECP through Form-29 within 15 days of the change. Failure to do so may result in outdated or inaccurate corporate records, affecting legal and financial proceedings. - 📊 Form-45 (Changes in Shareholding/Beneficial Ownership):
This form is used to disclose any changes in the company’s shareholding pattern or ultimate beneficial ownership. This has become increasingly important as part of anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) compliance. Filing Form-45 helps SECP and other regulatory authorities maintain transparency regarding who controls or benefits from a company. - 📑 Audited Financial Statements:
Public companies and large private companies that meet the audit threshold are legally required to prepare and submit audited financial statements each year. These statements must be reviewed by a registered Chartered Accountant and include a balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement, and notes to the accounts. These documents provide a fair and accurate representation of the company’s financial health and performance for the fiscal year.
Neglecting to file any of these forms on time can lead to a range of regulatory penalties, including financial fines, warning notices, or restrictions on company operations. In more serious cases, the SECP may mark the company’s status as inactive or non-compliant, which can block the company from opening bank accounts, renewing licenses, raising capital, or entering into contracts. It can also negatively impact the company’s reputation with investors, partners, and government bodies.
Understanding Financial Reporting Standards in Pakistan
All registered companies in Pakistan are required to prepare their financial statements in accordance with the applicable financial reporting framework. Depending on the nature and size of the business, companies must adhere to either the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) or the IFRS for SMEs (Small and Medium-sized Entities). These standards ensure uniformity, transparency, and reliability in financial reporting, making it easier for regulators, investors, and auditors to evaluate the financial health of an organization.
The choice of standard significantly influences how financial data is presented and interpreted. It affects:
- Balance Sheet Structure: Classification of current and non-current assets and liabilities, treatment of leases, provisions, and contingent liabilities.
- Profit and Loss Statement Classification: Revenue recognition methods, expense allocations, depreciation policies, and presentation of operating vs. non-operating income.
- Capital and Equity Disclosure: Share capital reporting, retained earnings treatment, and disclosure of shareholder equity movements.
Despite their importance, many small businesses find it challenging to implement and maintain financial reports that align with these complex standards. Without proper guidance, errors in classification or disclosure can lead to inaccurate tax filings or non-compliance during audits. Engaging a professional accounting firm like Arshad & Associates ensures that your financial statements are not only legally compliant but also strategically insightful.
Tax Deductions and Expense Recording
- Proper expense categorization is a critical component of effective tax planning and financial reporting. Businesses must ensure that all operational and capital expenses are correctly recorded in their accounting system under relevant heads to compute accurate taxable income and avoid overpaying income tax.
- Accurate and timely expense recording offers several key advantages:
- ✅ Precise Taxable Income Computation: Classifying expenses helps reduce net taxable profits and ensures only legitimate business income is taxed.
- ✅ Lower Income Tax Liability: Deductions such as depreciation, salaries, utilities, and rent can significantly reduce the overall tax burden.
- ✅ Better Audit Preparedness: Clear documentation and correct categorization provide transparency and reduce the risk of penalties during tax audits or financial reviews.
- To streamline this process, recurring expense categories should be set up in your company’s chart of accounts, including:
- Utilities (electricity, gas, water, internet)
- Rent (office or commercial space)
- Salaries & Wages (including bonuses and benefits)
- Marketing & Advertising (digital ads, promotions, branding)
Professional Fees (consultants, legal, accounting services)
Legal Entity Considerations
Your company’s legal structure directly impacts its tax obligations, filing requirements, and overall regulatory framework. Whether you operate as a sole proprietor, Single Member Company (SMC), or a Private Limited Company (Pvt Ltd), the compliance expectations and financial treatment can vary significantly.
Key differences based on entity type include:
- Withholding Tax Brackets: Corporations may be subject to different withholding tax rates when making payments for services, rent, salaries, or contractor fees.
- Annual Compliance Filings: Pvt Ltd and SMC entities must file statutory documents like Form-A, Form-29, and audited financial statements, while sole proprietors have simpler reporting requirements.
- Income Tax Slab Applications: The applicable income tax rates and exemptions depend on whether you are registered as an individual, AOP (Association of Persons), or company.
Choosing the right business structure at the outset is essential for long-term tax efficiency and operational flexibility. Consulting a qualified tax advisor or a firm specializing in accounting services for business ensures your company is correctly registered, well-structured, and optimized for compliance and profitability.
Bank Account & Audit Requirements
- In Pakistan, companies are required to maintain formal financial infrastructure to support transparency, traceability, and accountability. One of the first steps after incorporation is to open a dedicated business bank account, which can only be done with a valid National Tax Number (NTN) and incorporation documents such as the SECP registration certificate and company resolution.
- Key financial requirements include:
- Business Bank Account Setup: A separate account ensures clear segregation between personal and business finances and is essential for submitting income and sales tax returns.
- Transaction Record-Keeping for Bank Reconciliation: All business transactions must be tracked, recorded, and periodically reconciled with bank statements. This practice not only ensures accurate bookkeeping but also aids in detecting errors or fraud.
- Annual Audit Requirements: Companies that cross the revenue or asset threshold defined by SECP, as well as public limited companies, must undergo an annual audit conducted by a licensed Chartered Accountant. The audit verifies the accuracy of financial statements and assures stakeholders of the company’s fiscal health.
Common Problems Faced by Businesses
Running a business in Pakistan comes with a unique set of operational, financial, and regulatory challenges. Whether you’re a startup, SME, or an established company, navigating the complexities of tax compliance, bookkeeping, payroll management, and corporate governance can often become overwhelming—especially without expert guidance. Many businesses struggle to keep up with evolving regulations, meet statutory filing deadlines, or implement proper accounting systems. These issues not only impact financial performance but also increase the risk of penalties, audits, and reputational damage.
This section highlights some of the most frequent problems that Pakistani businesses face—ranging from poor record-keeping and delayed tax filings to software mismanagement and incorrect entity structuring—along with practical solutions to overcome them.
1. Poor Bookkeeping Practices
One of the most widespread issues among small and medium-sized businesses in Pakistan is the reliance on untrained or unqualified book keepers. While hiring low-cost staff may seem like a cost-saving move initially, it often leads to serious long-term consequences. Inaccurate bookkeeper accounting can result in missing or incorrect entries, unbalanced ledger accounts, and disorganized financial records. This lack of accuracy compromises the integrity of the general ledger, affects the reliability of financial reports, and leads to discrepancies during audits or tax filing. Poor bookkeeping also makes it difficult to prepare timely financial statements, track cash flow, or evaluate the company’s true financial position.
Partnering with a certified accounting services firm ensures that your books are maintained using double entry bookkeeping standards, financial statements are accurate, and compliance risks are minimized.
2. Late Income Tax Filing
Another common pitfall is late income tax filing or missing critical deadlines altogether. Many businesses either forget to file their returns or are unaware of their obligations under the Income Tax Ordinance, 2001. This is particularly risky when dealing with federal taxes, advance tax payments, or reporting on capital gains tax arising from asset sales or investments. Failing to file your income tax return on time not only results in monetary penalties and default surcharges, but can also lead to exclusion from the FBR Active Taxpayers List (ATL), which carries higher tax deduction rates and damages your professional credibility.
Timely filing through the FBR IRIS portal, along with professional oversight, helps businesses stay compliant and avoid unnecessary penalties.
3. Payroll Mismanagement
Handling employee compensation without a structured process is another challenge that causes both legal and operational issues. Many businesses still generate payroll slips manually or inconsistently, leading to errors in salary disbursement, withholding tax deductions, and statutory contributions such as EOBI and Social Security. Without a reliable payroll system, businesses risk underpaying or overpaying employees, misreporting payroll expenses, and failing to submit monthly tax and contribution statements.
Payroll mismanagement can trigger employee dissatisfaction, legal disputes, and non-compliance notices from regulatory authorities. Implementing a robust, cloud-based payroll management system, preferably integrated with accounting software, ensures that payroll is calculated accurately, taxes are deducted on time, and legal requirements are fulfilled.
4. Inadequate Use of Accounting Software
In today’s digital age, continuing to rely on outdated spreadsheets or manual bookkeeping significantly limits a business’s ability to scale. Many small businesses still hesitate to adopt modern solutions like QuickBooks Online, ZohoBooks, or Pastel Online Accounting, fearing high costs or technical complexity. However, manual systems are prone to human error, time-consuming, and lack the features needed for real-time insights, automation, and compliance reporting.
Failing to use accounting software not only hinders financial transparency but also makes tax filing, bank reconciliation, and performance analysis far more difficult. Adopting a modern software solution—paired with proper setup and training from experts—can dramatically improve productivity, reduce errors, and support data-driven decision-making.
5. Misunderstanding Taxation Laws
Tax laws in Pakistan are complex and regularly updated through Finance Bills and SROs. Unfortunately, many small and mid-sized businesses lack access to up-to-date knowledge about their tax obligations. Common areas of confusion include tax on rental income, income from capital gains, sales tax registration, and income tax withholding requirements under Sections 149 and 153. Misinterpreting or overlooking these laws can lead to underreporting, missed deductions, and legal exposure.
For instance, not knowing the correct withholding tax bracket to apply when paying a contractor or misunderstanding whether a particular supply is sales tax–exempt can cause regulatory breaches. Hiring a qualified tax advisor or consulting a reliable accounting firm ensures that your business adheres to relevant tax laws, maximizes allowable deductions, and avoids unnecessary liabilities.
Best Practices for Legal and Financial Compliance
Staying compliant with Pakistan’s corporate, tax, and financial regulations is essential for the long-term stability and credibility of any business. From timely tax filings and accurate bookkeeping to statutory SECP submissions and proper payroll management, legal and financial compliance ensures that your company operates within the boundaries of the law while maintaining investor and stakeholder confidence. As regulatory frameworks evolve and enforcement becomes more stringent, businesses must adopt structured, proactive approaches to avoid penalties, financial discrepancies, and reputational damage.
This section outlines key best practices that every business—regardless of size or industry—should implement to meet their compliance obligations effectively and efficiently, while also improving financial transparency and operational resilience.
Monthly Bookkeeping Review
Conducting a monthly bookkeeping review is essential for maintaining financial accuracy, identifying discrepancies early, and staying prepared for audits or tax filings. Businesses that fail to keep their books up to date risk data inconsistencies, cash flow issues, and incorrect reporting of income or expenses. The best way to ensure consistency and precision is to outsource bookkeeping services to qualified professionals who understand your industry, business structure, and compliance obligations.
Outsourcing helps streamline the bookkeeping entry process by ensuring that all financial transactions—sales, expenses, payroll, and vendor payments—are recorded accurately and in a timely manner. This also supports proper implementation of accrual accounting, where income and expenses are recorded when they are earned or incurred, not when the cash is exchanged. Monthly reviews also ensure that bank reconciliation is completed regularly, allowing businesses to match their bank statements with accounting records and detect any unauthorized or missed transactions before they become major issues.
Year-End Accounting Checklist
A smooth and compliant financial year-end process depends on timely execution of key accounting activities. Preparing in advance using a comprehensive year-end accounting checklist helps businesses close their books efficiently, avoid penalties, and confidently face tax filings or audits.
Essential steps include:
- ✅ Closing All Ledger Accounts: Finalize and balance all ledger accounts to ensure no transactions remain unrecorded. This includes income, expense, asset, and liability accounts.
- ✅ Reconciling Payroll and Filing WHT Returns: Review all payroll records, confirm correct salary disbursements, and ensure that withholding tax (WHT) has been deducted and deposited as required. Submit the necessary WHT statements to the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR).
- ✅ Completing Income Tax Return Submission: Prepare and file the annual income tax return via the FBR IRIS portal, including all supporting schedules, capital gains, and rental income declarations.
- ✅ Preparing for Audit with a Clean General Ledger: Ensure that the general ledger is fully reconciled and reflects accurate balances. Clear documentation and a well-maintained audit trail will support the audit process and reduce the risk of adjustments or fines.
This checklist not only ensures legal compliance but also enhances financial clarity and supports strategic planning for the next fiscal year.
Regular Payroll Audits
Regular payroll audits are a vital part of compliance and employee management. They help confirm that your payroll processes align with labor laws, tax regulations, and company policies. A well-executed payroll audit involves verifying that all employee records are complete and up to date, that payroll slips have been issued accurately, and that taxes such as income tax, EOBI, and Social Security have been properly calculated, deducted, and submitted.
Many businesses face payroll discrepancies due to manual errors, unstructured systems, or lack of knowledge about withholding tax obligations. These errors can lead to compliance risks, employee dissatisfaction, and financial penalties.
To reduce these risks and improve efficiency, businesses should adopt a modern payroll management system that automates salary calculations, applies the correct tax rates, generates payslips, and integrates directly with the company’s accounting software. Automation not only saves time but also enhances the accuracy and audit-readiness of your payroll process.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What’s the difference between bookkeeping and accounting?
Bookkeeping is the foundational process of systematically recording all daily financial transactions, including purchases, sales, receipts, and payments. It ensures that all transactions are accurately documented and categorized using the double-entry bookkeeping method. On the other hand, accounting is a broader and more analytical function. It involves interpreting, classifying, summarizing, and analyzing the data captured during bookkeeping to generate meaningful financial statements, ensure compliance, and support decision-making. While bookkeeping answers “what happened,” accounting helps you understand “what it means” for your business.
Q2: Do I need to file an income tax return if my company has no profit?
Yes, absolutely. Even if your business did not earn a profit or had zero revenue during the year, you are still legally required to file an income tax return with the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR). Filing your return confirms your business activity, keeps your National Tax Number (NTN) active, and ensures your company appears on the FBR Active Taxpayers List (ATL). Non-filing can result in higher withholding tax rates, penalties, and even suspension of your company’s registration status.
Q3: What is withholding tax and who needs to pay it?
Withholding Tax (WHT) is a tax that businesses are required to deduct at the time of making payments to suppliers, service providers, contractors, employees, or landlords. It is also referred to as tax deducted at source. Businesses act as withholding agents and must deduct the applicable tax rate from payments and deposit it with the government through designated FBR challans. Common transactions subject to WHT include salaries, rent, professional fees, contracts, and payments to non-resident entities. All registered businesses in Pakistan making such payments are legally obligated to deduct and deposit WHT in accordance with the Income Tax Ordinance.
Q4: Can I manage my payroll manually without software?
Yes, you can manage payroll manually, especially if you have a very small team. However, manual payroll processes are time-consuming and highly prone to calculation errors, missed deductions, and non-compliance with tax regulations. Using a payroll management system like QuickBooks Payroll, Xero, or ZohoBooks significantly improves efficiency, ensures accurate tax deductions (e.g., income tax, EOBI, Social Security), and automatically generates compliant payroll slips. These tools also integrate with your general ledger for accurate accounting and audit readiness, making them a smart investment for growing businesses.
Q5: What happens if I miss SECP or FBR filing deadlines?
Missing important compliance deadlines—whether for SECP statutory filings (like Form-A, Form-29, Form-45) or FBR tax returns—can result in serious consequences, such as:
- ❌ Financial Penalties and Surcharges for each day or month of delay
- ❌ Suspension or Revocation of Your National Tax Number (NTN)
- ❌ Company Being Listed as Inactive or Non-Compliant by SECP or FBR
- ❌ Legal Notices or Audits, increasing the risk of investigation or scrutiny
Timely filings are not just good practice—they are essential for maintaining operational continuity, financial credibility, and legal status.
Q6: What’s the benefit of outsourcing accounting and bookkeeping?
Outsourcing your accounting and bookkeeping to a professional firm like Arshad & Associates offers a wide range of benefits for both small and medium-sized businesses:
- ✅ Accuracy: Certified professionals ensure your financial data is recorded correctly using international standards and local compliance requirements.
- ✅ Timely Filings: Deadlines for tax returns, WHT, SECP forms, and financial statements are never missed.
- ✅ Legal Compliance: Experts stay up to date with evolving tax laws, financial reporting standards, and statutory requirements, reducing the risk of penalties or audits.
- ✅ Cost Efficiency: Gain access to experienced bookkeepers, tax consultants, and accountants without the expense of hiring full-time staff.
- ✅ Business Focus: Free up your internal team to focus on strategic growth instead of routine back-office tasks.
Outsourcing ensures that your finances are handled professionally while giving you the peace of mind to focus on running and growing your business.
How Arshad & Associates Can Help
At Arshad & Associates, we offer comprehensive solutions tailored to small and medium businesses across Pakistan.
Our Services:
- 📚 Bookkeeping and Accounting Services
- 💼 Payroll Management & Payslip Automation
- 🧾 Tax Preparation and Filing (FBR, WHT, SECP
- 📈 QuickBooks, Xero & ZohoBooks Setup & Support
- 🏢 Company Registration and Compliance Consulting
Why Choose Us:
- – Certified Experts in **bookkeeper accounting**
- – SECP & FBR compliance specialists
- – Support across all types of **accounting software**
- – Affordable plans for startups & SMEs
✅ Precision. Compliance. Growth.
Your Business Deserves More Than Just Numbers—It Deserves Confidence.
In the fast-paced world of business, even a small oversight in accounting, payroll, or tax compliance can lead to significant delays, penalties, or reputational damage. Whether you’re a startup navigating company registration in Pakistan, or a growing enterprise in need of reliable bookkeeping, income tax filing, or payroll management—Arshad & Associates is your trusted partner for long-term success.
🌟 Why Businesses Choose Arshad & Associates
- 📊 Certified Bookkeepers & Tax Advisors — With deep knowledge of SECP and FBR regulations
- 🧾 End-to-End Compliance Services — We handle Form-A, Form-29, WHT filings, and more
- 🔄 Seamless Software Integrations — QuickBooks, ZohoBooks, Xero, and IRIS e-filing systems
- 📦 Tailored Packages — Flexible plans to fit startups, SMEs, and established companies
- 💡 Transparent Pricing & Proactive Advice — No hidden fees. Just expert support when you need it.
📞 Let’s Take Your Business to the Next Level—Compliant, Accurate & Ready for Growth
Whether you’re overdue on your filings, unsure about FBR requirements, or want to digitize your entire back-office—we’re here to simplify, support, and scale your operations.
📍 Get in Touch Today
📞 Call: +92 331 5661278
📧 Email: info@localhost | talhaarshad97@gmail.com
🌐 Website: www.arshadassociates.com
🏢 Office: House 291, Street 17, Phase 5, Bahria Town, Islamabad
✨ Partner with Arshad & Associates—Where Precision Meets Peace of Mind.


